How to upgrade
Overview
The approach used to upgrade your Nextcloud Server depends on your installation type. This manual mainly focuses on the methods that apply to an Archive based installation. If you installed using Snap, Docker, a pre-built VM, or a package management tool then refer to the installation and update instructions for that installation method for the most accurate upgrading inststructions (generally located at the distribution point for the install method you chose).
There are two ways to upgrade an Archive based Nextcloud Server deployment:
With the Built-in Updater (via the web or command-line interfaces).
Manually upgrading (using a downloaded Archive file)
The Built-in Updater, in either Web or command-line mode, is the easiest choice for most environments. However some environments require the manual approach. Both approaches are covered fully here.
Important
Before upgrading, especially between major versions (e.g. v27.y.z -> v28.y.z) please review critical changes first. These are highlights of changes that may be required in your environment to accommodate changes in Nextcloud Server. These notes are periodically revised as needed so it is also a good idea to revisit them periodically, such as when proceeding with maintenance upgrades.
When an update is available for your Nextcloud server, by default you will receive a notification. You can also check for available updates by visiting the Update section under Administration settings->Overview in the Web UI.
Note
It is best to keep your Nextcloud server upgraded regularly. This means installing all maintenance/point releases and upgrading to new major releases before your current one reaches end-of-life status. Examples of major releases are 27, 28, or 29. Maintenance releases are intermediate releases for each major release that address critical functionality or security bugs. For example 28.0.4 and 29.0.2 are maintenance releases.
Approaching Upgrades
- Nextcloud must be upgraded step by step:
Before you can upgrade to the next major release, you need to upgrade to the latest point release of your current major version.
Then run the upgrade again to upgrade to the next major release’s latest point release.
You cannot skip major releases. Please re-run the upgrade until you have reached the highest available (or applicable) release.
Example: 18.0.5 -> 18.0.11 -> 19.0.5 -> 20.0.2
Wait for background migrations to finish after major upgrades. After upgrading to a new major version, some migrations are scheduled to run
as a background job. If you plan to upgrade directly to another major version (e.g. 24 -> 25 -> 26) you need to make sure these
migrations were executed before starting the next upgrade. To do so you should run the cron.php file 2-3 times, for example:
$ sudo -u www-data php -f /var/www/nextcloud/cron.php
For more information about background jobs see Background jobs.
Upgrading is disruptive. Your Nextcloud server will be put into maintenance mode, so your users will be locked out until the upgrade is completed. Large installations may take several hours to complete the upgrade. Nevertheless usual upgrade times even for bigger installations are in the range of a few minutes.
Warning
Downgrading is not supported and risks corrupting your data! If you want to revert to an older Nextcloud version, make a new, fresh installation and then restore your data from backup. Before doing this, file a support ticket (if you have paid support) or ask for help in the Nextcloud forums to see if your issue can be resolved without downgrading.
Update notifications
Nextcloud has an update notification app, that informs the administrator about the availability of an update. Then you decide which update method to use.
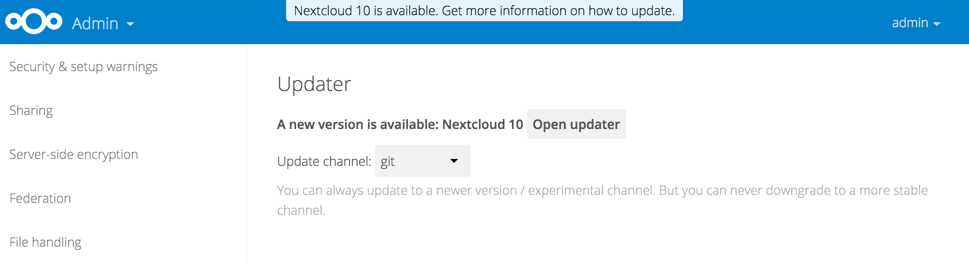
Figure 1: The top banner is the update notification that is shown on every page, and the Updates section can be found in the admin page
From there the web based updater can be used to fetch this new code. There is also an CLI based updater available, that does exactly the same as the web based updater but on the command line.
Prerequisites
See also
If you upgrade from a previous major version please see critical changes first.
You should always maintain regular backups and make a fresh backup before every upgrade.
Then review third-party apps, if you have any, for compatibility with the new Nextcloud release. Any apps that are not developed by Nextcloud show a 3rd party designation. Install unsupported apps at your own risk. Then, before the upgrade, all 3rd party apps must be disabled. After the upgrade is complete you may re-enable them.
Maintenance mode
You can put your Nextcloud server into maintenance mode before performing
upgrades, or for performing troubleshooting or maintenance. Please see
Using the occ command to learn how to put your server into
the maintenance mode (maintenance:mode) or execute repair commands
(maintenance:repair) with the occ command.
The built-in Updater does this for you before replacing the existing Nextcloud code with the code of the new Nextcloud version.
maintenance:mode locks the sessions of logged-in users and prevents new
logins. This is the mode to use for upgrades. You must run occ as the HTTP
user, like this example on Ubuntu Linux:
$ sudo -u www-data php occ maintenance:mode --on
You may also put your server into this mode by editing config/config.php.
Change "maintenance" => false to "maintenance" => true:
<?php
"maintenance" => true,
Then change it back to false when you are finished.
Manual steps during upgrade
Some operation can be quite time consuming. Therefore we decided not to add them to the normal upgrade process. We recommend to run them manually after the upgrade was completed. Below you find a list of this commands.
Long running migration steps
From time to time we do some changes to the database layout that take a lot of time, but can be executed while Nextcloud stays online. Thus we moved them into a separate command that an administrator can execute on the CLI without the need to lock the instance into maintenance mode (at least for some of them). The instance will also work without those changes applied, but performance is improved significantly by them. There is also always an hint in the setup checks of the admin settings web interface.
Those include for example:
$ sudo -u www-data php occ db:add-missing-columns
$ sudo -u www-data php occ db:add-missing-indices
$ sudo -u www-data php occ db:add-missing-primary-keys
You can use the --dry-run option to output the SQL queries instead of executing them.